CFD COMPUTATIONALFLUID DYNAMICS
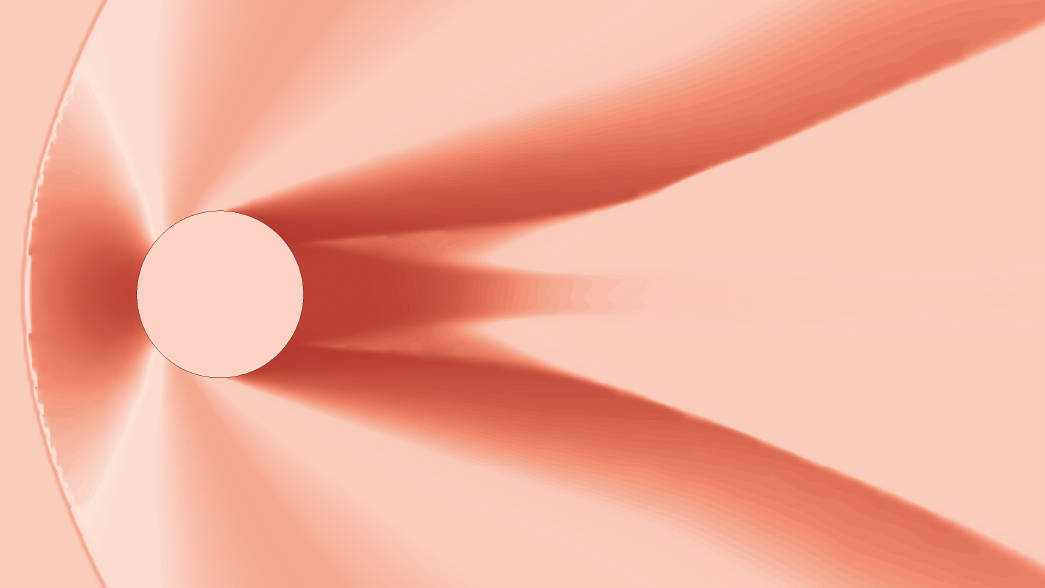
The CFD allows you to simulate numerically with the aid of a computer the fluid dynamic behaviour and thermo-fluid dynamics of single components, complex process equipment and cleanrooms. Through numerical simulation it is possible to govern the design activity and anticipate outcomes, drastically reducing the risk of errors. This capability is all the more important today, given the ever-increasing complexity of projects which must combine a high degree of quality with the increasingly current issues of energy saving.
Sustainability
The fluid dynamics simulation, as part of the design of the HVAC systems serving the cleanrooms, makes it possible to optimize the choice and positioning of the air diffusion and recovery systems, maximizing their ventilation effectiveness, with important impacts on the reduction of consumption and hence the associated ventilation costs.
Quality by design
Fluid dynamics simulation makes it possible to analyze and fully understand the behaviour of a cleanroom and its discrete systems, allowing more awareness of use and raising the quality level of the final product.
Design Project simulation
To analyze critical aspects, optimizing times and costs.
Troubleshooting
Analisi del comportamento dei sistemi esistenti per identificare cause di malfunzionamenti.
Contamination control strategy
L’analisi dei flussi d’aria nei vari scenari operativi e la comprensione degli stessi svolgono un ruolo fondamentale nell’implementazione di una strategia vincente di controllo della contaminazione, consentendo di predisporre le azioni correttive più efficaci in caso di evento avverso.
Sostenibilità
La simulazione fluidodinamica, nell’ambito del progetto dei sistemi HVAC a servizio delle cleanrooms, permette di ottimizzare la scelta ed il posizionamento dei sistemi di diffusione e ripresa dell’aria, massimizzandone l’efficacia di ventilazione, con impatti importanti sulla riduzione dei consumi e quindi dei costi di ventilazione associati.
Quality by design
La simulazione fluidodinamica permette di analizzare e di comprendere a fondo il comportamento di una cleanroom e degli impianti ad essa dedicati, consentendone un uso più consapevole ed elevando il livello della qualità del prodotto finale.
Progettazione
Simulazione del progetto per analizzare gli aspetti critici, ottimizzandone tempi e costi.
Contamination control strategy
The analysis of the air flows in the various operational scenarios and their understanding play a fundamental role in the implementation of a successful contamination control strategy, allowing the preparation of the most effective corrective actions in the case of an adverse event.
Troubleshooting
Analysis of the behavior of existing systems to identify causes of malfunctions.