BIM, LASER
SCANNER & CDE
BIM, LASERSCANNER & CDE
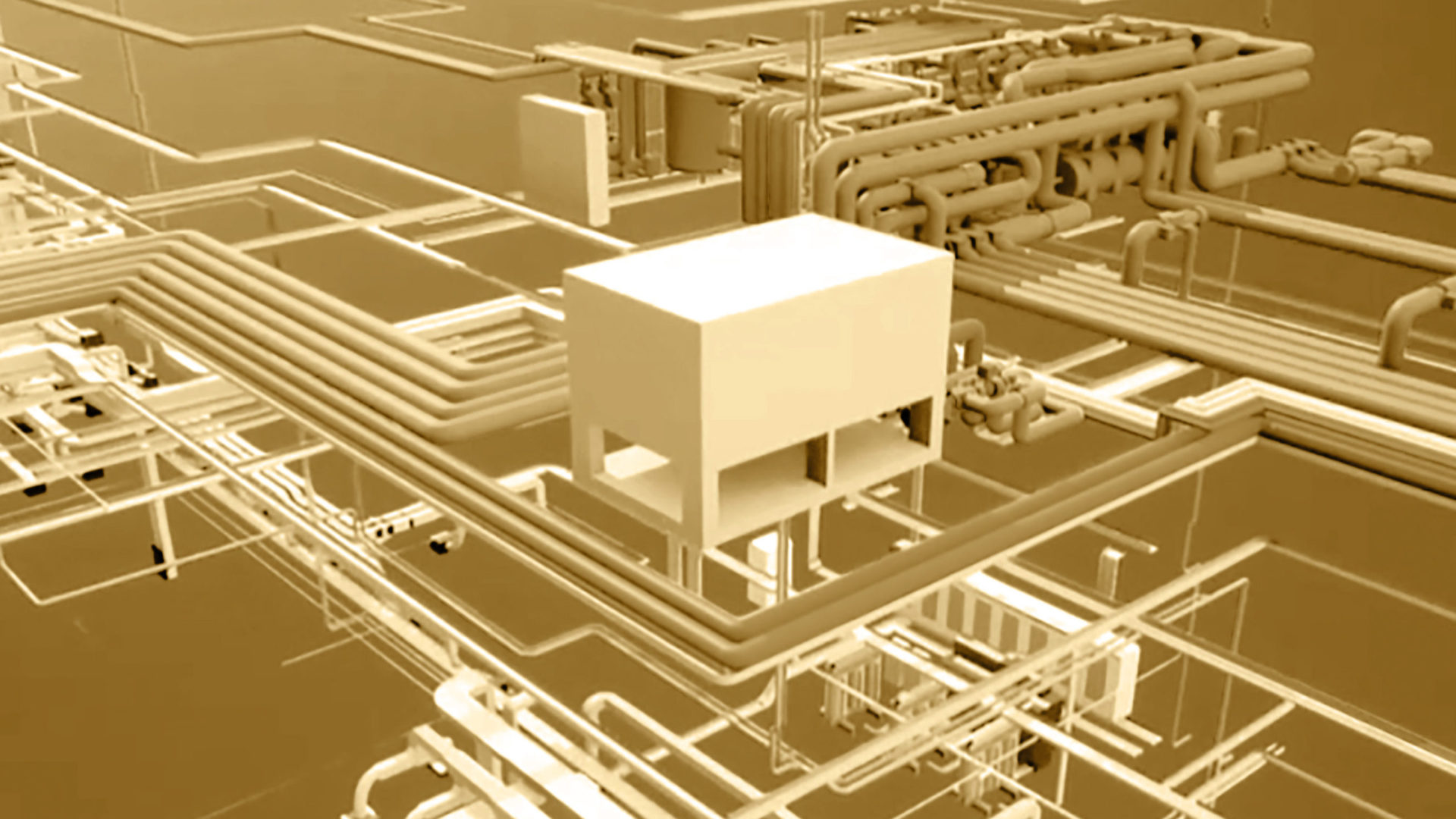
BIM
A method of integrated design which allows the optimization and updating of its constituent elements during the entire project life cycle. It can be perfectly applied both in existing contexts and in new operations.
The advantages of BIM
Design visualization
Construction of a 3D model with very high adherence to the final realization.
Design options
Higher design quality standards, in every respect.
Clash detection
Reduction of lead times and subcontractor changes.
Constructability review
Effective review of the implementation, according to the defined parameters.
Costs
All 4D elements are connected with the relative resources, to define the final costs and each project phase.
Sustainability
All the building systems are evaluated in terms of energy management, recovering information on the elements that make up the different moments of the building’s life cycle.
Facility management
The adoption of BIM and its ability to model object databases in 3D revolutionizes many of the maintenance processes and allows us to integrate the life cycle of a building.
Occupational safety and health
The use of BIM in the 3rd and 4th dimension modifies the management of H&S processes, favouring risk reduction and coordination of activities.
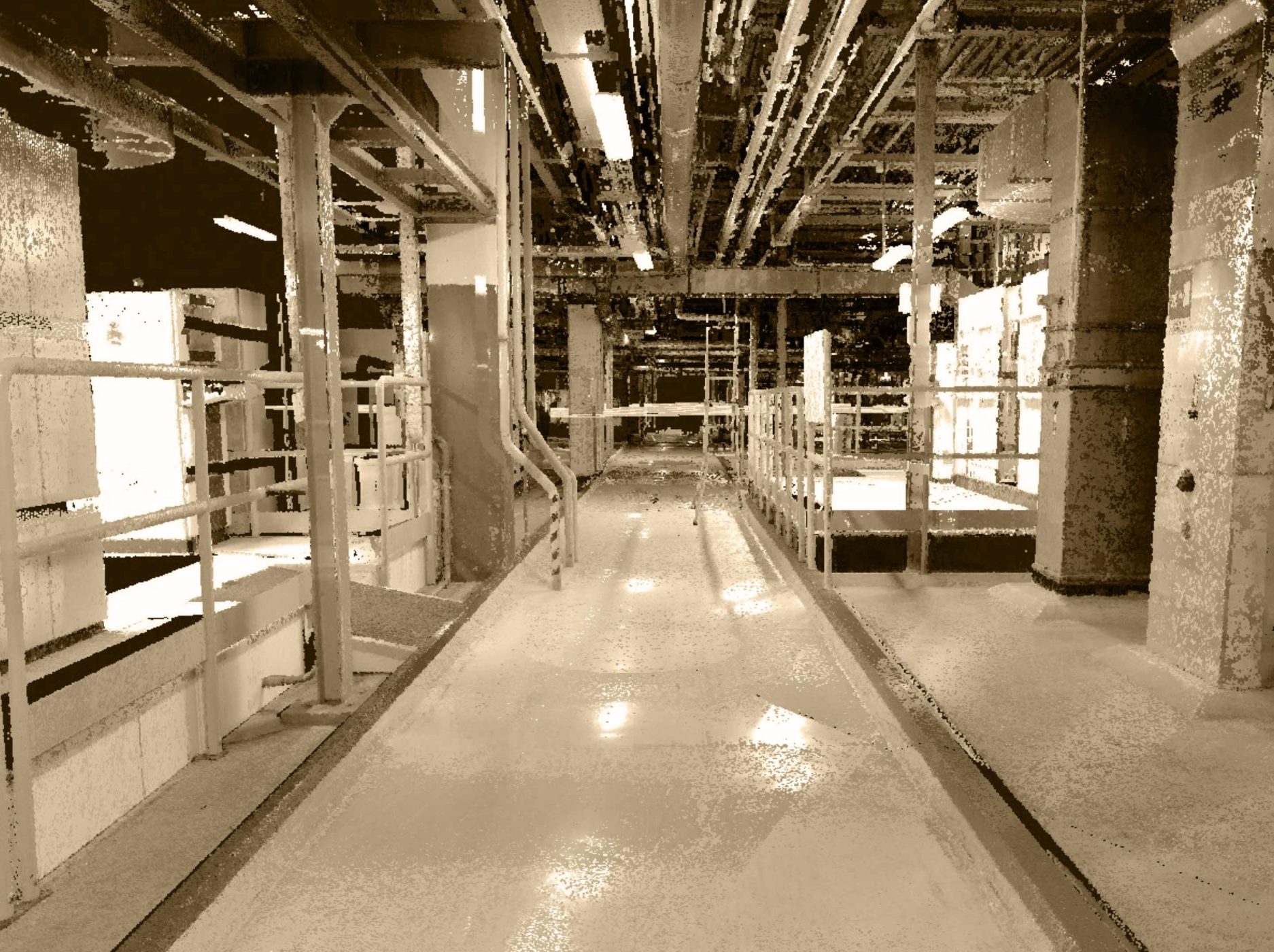


LaserScanner
Thanks to this tool scans of internal and external environments of the building, can be performed, obtaining a point cloud which will then be post-produced via software in order to create a floor plan in 2D or 3D format.
Advantages
— Optimization of execution times
— Accuracy of relief measurements carried out
— Cost reduction compared to a standard survey
CDECommon DataEnvironment
We use Autodesk Construction Cloud as a platform for collecting and sharing project documents.
Advantages
— All parties involved in a project actively work together
— Document sharing, transmission and review processes are optimized
— Management time savings
— A real history of the project is created, available for consultation at any time.